Sub-GHz (IEEE 802.15.4) vs. LoRaWAN: Comparing Two Pillars of IoT Communication


Sub-GHz (IEEE 802.15.4) and LoRaWAN are prominent technologies in wireless communication. Each offers unique features and applications, from long-range, low-power data transmission to robust connectivity in diverse environments. Understanding the differences between Sub-GHz (IEEE 802.15.4) and LoRaWAN is crucial for optimizing their use in various Internet of Things (IoT) projects
Sub-GHz (IEEE 802.15.4) Technology
IEEE 802.15.4 is a standard for low-rate wireless personal area networks (LR-WPANs), designed to provide low-cost, low-power communication for devices that often operate on batteries. It can use different frequency bands, including sub-GHz (868/915 MHz), which helps it communicate over longer distances while using less power. These frequencies are often used for long-range communication due to their ability to penetrate obstacles and cover greater distances compared to higher frequency bands like 2.4 GHz.
Key Features of Sub-GHz:
- Frequency Band:
Sub-GHz (IEEE 802.15.4) operates in the Sub-GHz frequency range, typically around 433MHz, 868MHz in Europe and 915MHz in North America. This frequency band is less crowded than the 2.4GHz band, reducing interference.
- Range:
It supports short to medium-range communication, generally up to a few hundred meters. This makes it suitable for applications within confined areas.
- Data Rate:
The Data rates range from 20 to 250kbps, balancing speed and power consumption.
- Network Topology:
Often used in mesh networks, where devices can relay data to extend the network range. This topology enhances network reliability and coverage.
Applications:
- Home Automation:
Smart lighting, security systems, and energy management.
- Industrial Monitoring:
Machine health monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process control.
- Smart Utility Networks:
Smart metering for electricity, water, and gas.
Example Modules:
- TI CC1310:
Features a sub-GHz transceiver and an ARM Cortex-M3 MCU, offering low power and high performance.
- Atmel AT86RF215:
Dual-band transceiver supporting both sub-GHz and 2.4 GHz bands, suitable for diverse applications.
LoRaWAN Technology
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a communication protocol specifically designed for IoT applications. It operates on sub-GHz frequencies and is managed by the LoRa Alliance. LoRaWAN defines the communication protocol and system architecture for the network, ensuring efficient data transmission between devices and gateways.
Key Features of LoRaWAN:
- Frequency Band:
LoRaWAN utilizes various sub-GHz frequency bands, including license-free bands, which helps in reducing interference.
- Range:
Known for its long-range capabilities, supporting communication over several kilometers. This makes it ideal for wide-area applications.
- Data Rate:
Provides lower data rates, typically up to 50 kbps, but is optimized for low power consumption.
- Network Topology:
Employs a star-of-stars topology, where end devices communicate with gateways that forward data to a central network server.
Applications:
- Smart Cities:
Street lighting control, waste management, and parking sensors.
- Agriculture:
Soil moisture monitoring, crop health tracking, and livestock management.
- Asset Tracking:
Real-time location tracking of goods and equipment.
- Environmental Monitoring:
Air quality sensors, weather stations, and water quality monitoring.
Example Modules:
- Semtech SX1276:
A widely used LoRa transceiver module, known for its long-range communication and low power consumption.
- Murata CMWX1ZZABZ:
A compact LoRaWAN module with an integrated MCU, offering a complete solution for IoT applications.
Choosing the Right Technology
When deciding between Sub-GHz and LoRaWAN, consider the following factors:
- Range and Coverage:
If long-range communication and better penetration are priorities, Sub-GHz (IEEE 802.15.4) might be the better choice.
- Network Management:
For extensive IoT deployments requiring robust network management, LoRaWAN offers more comprehensive solutions.
- Power Consumption:
Both technologies are energy-efficient, but specific use cases might favor one over the other based on device requirements.
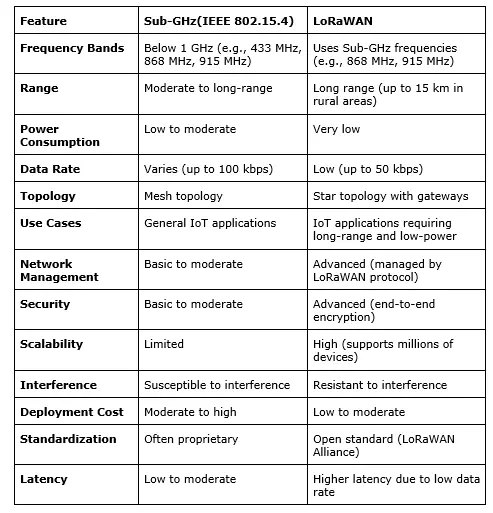
Here’s a comparison chart to highlight the key differences between Sub-GHz and LoRaWAN:
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Sub-GHz (IEEE 802.15.4) and LoRaWAN offer significant benefits for enhancing effectiveness in various applications. By understanding their differences and applications, businesses and individuals make informed decisions to create smarter, more efficient environments. At IOSCAPE, we utilize these technologies in our IoT products to enable long-range communication, reduce costs through star/mesh topology, and extend the battery life of battery-operated devices.